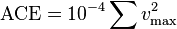Yesterday marked the official start to the 2014 Atlantic Hurricane season (June 1 – November 30), so this is as good a day as any to talk about the forecast for this season. The graphic below shows the National Hurricane Center’s official 2014 Hurricane Season Outlook that was released last month. This forecast is probabilistic, i.e. it gives a range of numbers and chances that this season will either exceed or fall below the forecast total.

Explanation
In the NHC’s parlance, Named Storms refers to tropical or subtropical storms that produce sustained winds in excess of 39mph (this is the criteria for a tropical or subtropical storm) at any point in their life cycle. Hurricanes refer to the named storms that end up producing sustained winds in excess of 74mph, and Major Hurricanes refer to hurricanes that make it to Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson classification scale. Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) is a rough measure for the overall intensity of a tropical cyclone and is calculated as follows:
The ACE of a season is calculated by summing the squares of the estimated maximum sustained velocity of every active tropical storm (wind speed 35 knots (65 km/h) or higher), at six-hour intervals. Since the calculation is sensitive to the starting point of the six-hour intervals, the convention is to use 0000, 0600, 1200, and 1800 UTC. If any storms of a season happen to cross years, the storm’s ACE counts for the previous year.[2] The numbers are usually divided by 10,000 to make them more manageable. The unit of ACE is 104kn2, and for use as an index the unit is assumed. Thus:
where vmax is estimated sustained wind speed in knots. (Source – Wikipedia)
Hence, a high ACE number corresponds to a very intense storm or storm(s).
Outlook
As you can see from the above image, the NHC is calling for a normal to slightly below normal season for the Atlantic with 8-13 named storms, 3-6 hurricanes, and 1-2 major hurricanes. Despite the fact that the forecast calls for a normal to below normal season, it only takes one landfalling hurricane or major hurricane to inflict serious damage to a coastal area. Even with just tropical storms, huge amounts of rain can fall leading to major flooding.
El Niño’s Impact
One of the reasons why the forecast is calling for a normal to below normal season is that it appears an El Niño event is initiating and forecast to increase in intensity. El Niño refers to a phenomenon that occurs when the ocean surface of the Eastern Pacific Ocean becomes abnormally warm (La Niña refers to the opposite effect, when the Eastern Pacific cools abnormally).
This anomalous warming of the Eastern Pacific leads to all sorts of global climate impacts. Among these is a noticeable decrease in the incidence of Atlantic hurricanes, and an increase in the number of Eastern Pacific hurricanes. In fact, you can see in the same outlook, NHC is calling for a near normal to above normal hurricane season for both the Eastern and Central Pacific. The reason behind this is simple: hurricanes feed on heat to grow, so the warmer the water below a storm, the greater the potential for that storm to grow.

As you can see from the map above, there is a region of abnormally warm sea surface temperatures extending west into the Eastern Pacific from the coast of Ecuador and Peru (yellow & orange). At the same time, there is a large area of much cooler than normal sea surface temperatures extending from the west coast of Africa into the Central Atlantic (light and dark blue). Incidentally, these cool temperatures off the coast of Africa are in a region that is notable for spawning some of the strongest hurricanes, the Cape Verde type hurricane. Clearly, if this temperature anomaly keeps up, it will serve to inhibit the formation of tropical storms and hurricanes in that region.